▲
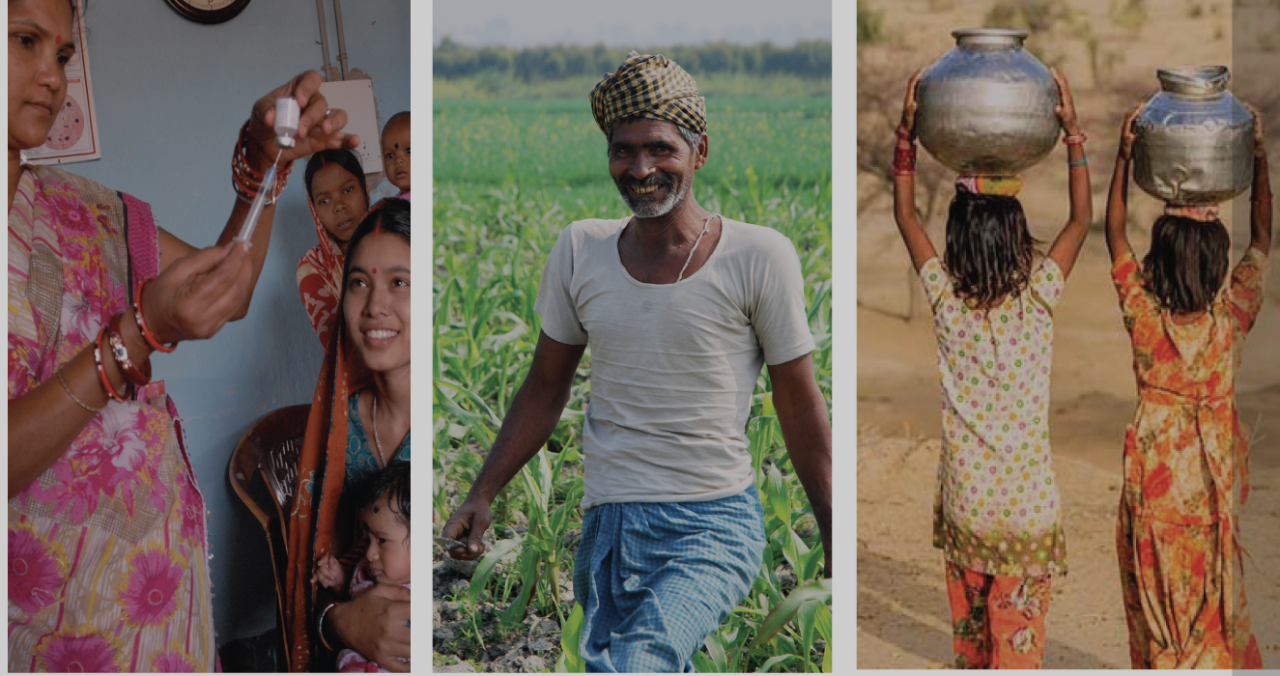


Diagnostics for rural India
The penetration of diagnostic services in India is mainly concentrated around metros and big cities. In rural India, the access to healthcare is restricted to primary health centres catering just the basic healthcare services. Typical health problems in rural India are related to nutritional deficiencies, lack of maternal and perinatal condition support, common occurrence of communicable diseases such as malaria, diarrhea, tuberculosis, and respiratory diseases. Shortage of hygiene infrastructure, lack of awareness, limited access to facilities, lack of trained medical personnel, dearth of medicines and good doctors are the key challenges faced by more than 70 percent of India’s population living in rural areas today.
The India-Israel Bridge is seeking “low fidelity, high frequency” solutions for diagnostics in rural India. The solutions will focus on cheap, low fidelity hardware that can capture recurring diagnostic data at a high frequency, and use machine learning and algorithmic data manipulation to accurately diagnose and predict conditions.
Clarifying remarks not for website: Key technology here is the lack of “ Low cost Intelligent ,Reliable, Connected” devices that would resolve the problem of Non-Accessibility of affordable healthcare to this segment of population. “Intelligence” in the device should enable easy training to the “Low skilled” resources in the rural areas while “ Connectivity” should help them to access the experts in Tier 1 & Tier 2 cities .
NCDs
Every year, roughly 5.8 million Indians die from heart and lung diseases, stroke, cancer and diabetes. In other words, 1 in 4 Indians risks dying from an Non-Communicable Disease (NCD) before they reach the age of 70. India stands to incur a loss of $4.58 trillion between 2012 and 2030 due to NCDs.
India faces the human and economic threat posed by NCDs. Cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases, diabetes, and other NCDs are estimated to account for 60% of all deaths in India, making them the leading cause of death – ahead of injuries and communicable, maternal, prenatal, and nutritional conditions. Furthermore, NCDs account for about 40% of all hospital stays and roughly 35% of all recorded outpatient visits.
NCDs are caused, in part, by underlying, modifiable risk factors. The major risk factors for NCDs in India are tobacco use, harmful use of alcohol, lack of physical activity, and a poor diet.
Poor compliance to diet and to drug regimens, lack of exercise, unhealthy living standards and medical therapy in patients with NCD increase the risk of complications and death.
We are seeking high quality, innovative solutions that are affordable, accessible and sustainable, focusing on constant and real time health monitoring, home care, remote care, periodic counseling and advice on health management. This needs to take into account the existing technology and infrastructure in India, demand creation and service delivery.
Clarifying Remarks not for website: Fundamentally the challenge here is to move from a Reactive healthcare system to Preventive Healthcare system which will require “Affordable” & “Smart” ,devices for Screening of critical parameters on an a periodical manner and “Intelligent Alert systems” to patients, care givers and experts in case of a warning episode with the Patient.
Your password must contain atleast:
* Your password must contain atleast:
Please Complete Your Profile to Access This.
Startup India Portal is a one of its kind online platform for all stakeholders of the startup ecosystem in India.




Forgot your Password
Please Enter Your OTP Password sent on your Email Id
Please change your password