Planning is often seen as the antithesis to growth in start-up circles. What is often mistaken though is the essentiality of strategic planning in the long term success of any venture.
What is the need of Strategic Start-up Planning?
A strategic plan is defined as a number of steps or strategies that a company must identify and employ to meet its set objectives.
Often new start-ups are able to increase sales rapidly and climb the growth curve but reach a point of stagnation. Strategic planning serves exactly this purpose, to maintain as well as continue this growth by defining a path and evaluating its success in specific intervals. It is critical in prioritizing resources to increase the return on investment. Also its seen as a plus point by VCs during the funding process as it indicates clarity of goals. Lastly it serves as a great source of motivation for all members of a start-up.

Difference between Strategic Plans and Business Plans
Despite being a type of business plan, strategic plans have many dissimilarities. While the business plan of a start-up is a written plan of the business model, detailing every aspect of the business and is usually created in the initial days of the venture.
In contrast a strategic plan is primarily used for providing strategic direction for an existing organization. These plans are usually created in more established ventures. The larger a venture gets the more severe the need for strategic plans gets. Another common misconception that planning is a static activity exists whereas in reality for successful optimization strategic plans need to be seen as fluid documents.
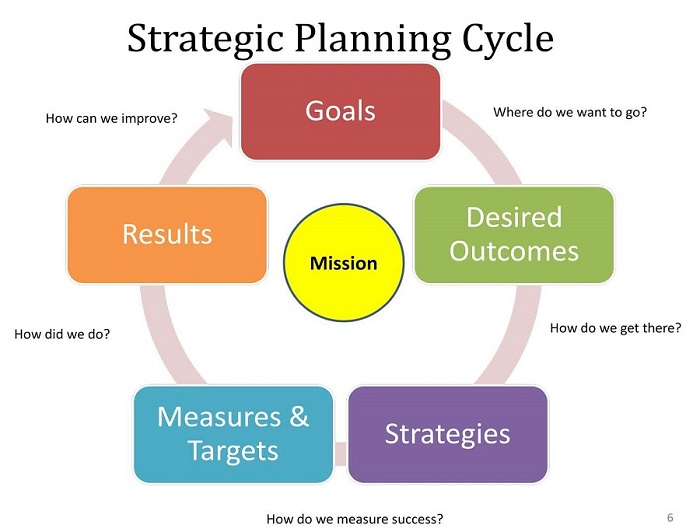
Components of Strategic Planning-:
- Vision: The vision of a company is what it wants to become or achieve in the future. It is the driving force of the business. Key questions like these will help you understand your vision better – Who is the customer? What business are you in? How do you want to grow? What is your Competitive Advantage?
- Values: The company’s values are nothing but the beliefs and principles it wants to promote and espouse. Values are seen as guiding principles that never change. It may be useful to type out a core value statement.
- Mission Statement: A mission statement states the underlying incentive for firms to do business. It is not a part of strategic planning, rather creates the base for strategic objectives to be made from. The difference between this and the vision is that the mission statement does not project a goal for the future.
- Goals: These are the desired results of the effort put in. Start-up coach Cate Costa describes the best goals as, “SMART goals – that is, they should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound.” So rather than saying you want to increase your sales drastically, say you want to increase your sales by 25% in the next 12 months. Further divisions should be made to a ventures goals, namely-
>Short term goals – 6 months to 1 year
>Long term goals – 1 year to 5 year
- Competencies: Each venture would have some process that they specialize in, while some which can be done better by others. These activities that the firm is exceptional at are called its core competencies. This step helps in achieving goals by providing a point to start on. For maximum effectiveness a start-up should do an honest assessment of its capabilities and skills.
- Evaluation: This forms the last step of strategic planning where all the steps and methods of evaluating goals is stated. Performance indicators like KPIs (key performance indicators) which evaluate the success of an organization or of a particular activity in which it engages can be used. This step ends with the evaluations leading to adjusting and creating new goals for the venture and the cycle continues.