ढल जा नमुना
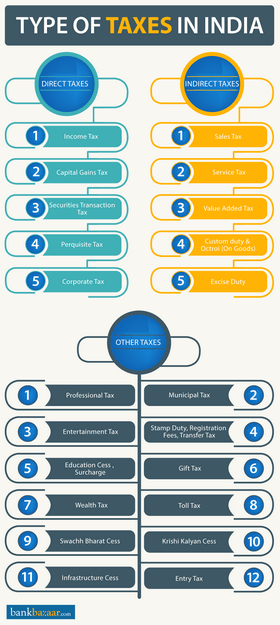
Taxes are of two distinct types: direct and indirect taxes. विछोटियूं इंदु आहिनि जहिं वाटि सां इहे ढलयूं लागु कयूं वेंदयूं आहिनि. Some are paid directly by you, such as the dreaded income tax, wealth tax, corporate tax, etc., while others are indirect taxes, such as the value-added tax, service tax, sales tax, etc.
- सिधी ढलयूं
- अणसिधा ढलअ
But, besides these two conventional taxes, there are also other taxes that have been brought into effect by the Central Government to serve a particular agenda. ‘Other taxes’ are levied on both direct and indirect taxes, such as the recently introduced Swachh Bharat Cess tax, Krishi Kalyan Cess tax, and infrastructure Cess tax, among others.
1. सिधा ढल
Direct taxes, as stated earlier, are taxes that are paid directly by you. These taxes are levied directly on an entity or an individual and cannot be transferred onto anyone else. One of the bodies that overlooks these indirect taxes is theCentral Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), which is a part of the Department of Revenue. It has, to help it with its duties, the support of various acts that govern various aspects of direct taxes.
इन मां के कानुन:
आमदनी ढल कानुन:
इहा पिणि जाणि वेंदी आहे 1961 जे आई टी कानुन तोर ऐं नियम जी पक कंदी आहे जो कि भारत जे कमाई ढल खे तरतीब कंदो आहे. The income, which this act taxes, can come from any source, like a business, owning a house or property, gains received from investments and salaries, etc. ही इहो कानुन आहे जो पक कंदो आहे केतरी ढल फाईदो पीक्स डिजाजिट ते मिलिंदी या केजिरो जीवन बिमे जी किस्त ठहिंदी. It is also the act that decides how much of your income you can save through investments and what the slab for the income tax will be.
मलिकियत ढल कानुन:
The Wealth Tax Act was enacted in 1951 and is responsible for the taxation related to the net wealth of an individual, a company, or a Hindu Unified Family. मलिकियत ढल जी सहुले में सहुली गणत इहो हो त जेकर मुल मलिकित रुपया 30 लख में वधिक हुजे त पोई 1% उन राशी जी जेका 30 खां वधिक हुजे सां ढल तोर भूगतान कबो. इहो बंद कयो वयो हो 2015 साल में बजेट दौरान. तहिं महल खां इन खे मटयो वयो आहे वाधारो वसुली सां जे कि 12% आहे शख्सनि लाई जो कि 1 किडेड सालानो खां वधिक कमाअन था. इहो पिणि लागु थिंदो उन कम्पनीयूंनि ते जिनि खे सालानो ढल रुपया 10 किडोड खां मथे आहे. The new guidelines drastically increased the amount the government would collect in taxes as opposed to the amount they would collect through the wealth tax.
Gift Tax Act:
The Gift Tax Act came into existence in 1958 and stated that if an individual received gifts, monetary or valuable, as gifts, a tax was to be paid on such gifts. The tax on such gifts was maintained at 30%, but it was abolished in 1998. Initially, if a gift was given and it was something like property, jewellery, shares, etc., it was taxable. According to the new rules, gifts given by family members like brothers, sisters, parents, spouses, aunts, and uncles are not taxable. Even gifts given to you by the local authorities are exempt from this tax. How the tax works now is that if someone, other than the exempt entities, gifts you anything that exceeds a value of Rs. 50,000, then the entire gift amount is taxable.
खर्चु ढल कानुन:
हिउ हिकु कानुन आहे जो कि 1987 में वजूद में आयो ऐं इहो तव्हां जे हिक शख्स जे रुप में होटल या रेसटुरेंट में हासिल कयसु वेवायूं ते कयलु खर्च सा वासतो थो रखे. इहो समुरे भारत में लागु आहे ,वाई जम्मु ऐं कशमीर जे. इहो पधिरो थो करे त खर्च ते वसुली कई वेंदी हिन कानुन हेटि जेकरि इहो रुपया 3 खां वधिक थिंदा, 000 होटलनि लाई ऐं समुरी वसुली जो कि रेस्टुरेंट में खर्च थिया हुजिनि.
वयाज ढल कानुन:
1974 जो वयाज ढल कानुन खास खसुसी हालितुंन में वयाज जी कमाई ते मथोुं ढल सां लागापो रखिंदो आहे. In the last amendment to the act, it was stated that the act does not apply to interest that was earned after March 2000.
हेटि मिसाल था डि॒जिनि समुरे धार धार नमुने जे सिधे ढल जा:
सिधी ढल जा मिसाल
उते कजहि सिधा ढल आङिनि जो कि तव्हां भरिंदा आहियो
a) आमदनी ढल:
हिउ सभिनि खां वझी जातलु ऐं घटि समिझयलु ढल आहे. It is the tax that is levied on your earnings in a financial year. हिते जाम वधिक पासा आङिनि कमाई ढल खे जिअं कि ढल स्तर, ढलाईती कमाई, मुंद ते ढल कटाई (टी डी ऐस), डलाईते कमाई मंझ घटाई वगिराह. ढल लागु थिंदी आहे बि॒नहिनि शख्सअनि तोडे कम्पनीयूंनि ते. शखसनि लाई, जा ढल खेनि बुगतान थी करणी पवे सा दारुमदार ती रखे उन ढल जे भाङे में जहिं में हो किरन था. हिउ ब्रेकेट या स्तर पक कंदो आहे भूगतान कंदड ढल जो जोकि आधारित आहे कथ कंदड जे सालाने कमाई ऐं इहा बो॒डी ढल खां 30% ढल थी ती सघे वधीक कमाई गिरोह लाई.
The government has fixed different tax slabs for varied groups of individuals, namely general taxpayers, senior citizens (people aged between 60 to 80, and very senior citizens (people aged above 80).
b)Capital Gains Tax:
इहा हिक ढल आहे जहिं जो भूगतान करणो पवंदो आहे जड॒हिं तव्हां रुपयनि जी का वडा॒ राशी हासिल कंदा आहियो. इहा हिक पुंजीसेडहायप या मलिकियत जो विकरे मां थी ती सघे. इहो घणो करे बिन नमुनि जा थिंदा आहिनि, नंढे अर्से जा सरमाऐ जी हासिलियत 36 महिनि खां घटि सेडहायप खां ऐं ढिघे अर्से जी सरमाऐ जी हासिलियत जो कि 36 महिनि खां वधीक सेडहायप कजे थी. The tax applicable for each is also very different since the tax on short term gains is calculated based on the income bracket that you fall in and the tax on long term gains is 20%. The interesting thing about this tax is that the gain doesn’t always have to be in the form of money. It could also be an exchange in kind, in which case the value of the exchange will be considered for taxation.
c) तहफूज डे॒तीलेती ढल:
इन में का बि गु॒जायप नाहे जे जेकरि तव्हां खे जा॒णि आहे त किअं स्टाक शेअर बाजार ऐं तहपूज में वेपार कजे, तव्हां जाम पैसा कमाऐ था सघो. This too is a source of income, but it has its own tax, which is known as the Securities Transaction Tax. किअं हिउ ढल मडही वेंदीआहे शेअर जे किमत खे गंढण बैदि. हिन जो मसलबु इहो आहे त हर वक्त तव्हां शेअर खरिदो या विकणो, तव्हां खे ढल जो भुगतान करणो पवंदो. समुरी वेपारित तङफूजनि खे बारतीय स्टाक ऐंकसेंचेंज मथसि इहा ढल खेनि गंढियलु आहे.
घ) लापो ढल:
लापो समुरा फाईदा या सहुलितयूं थिंदयूं आहिनि जो कि मालिक मुलाजिमनि खे आछिंदो आहे. हिउ हक कम्पनीअ पारां मेसर कयलु घरु या गा॒डीअ जे सुधा आहिनि तव्हां जे इस्तमाल लाई. These perks are not just limited to big compensation like cars and houses; they can even include things like compensation for fuel or phone bills. किअं इहा ढल मडही वेंदी आहे इहो डाचे त इहो पार्क हासिल कयो वयो आहे कम्पनी पारा ंया मुलाजिम पारां इस्तमाल थियो आहे. In the case of cars, it may be so that a car provided by the company and used for both personal and official purposes is eligible for tax, whereas a car used only for official purposes is not.
e) कार्पोरेट ढल:
कार्पोरेट ढल कमाई ढल आहे जो कि कम्पनीयबंनि पारां डि॒ञो वेंदो आहे उन उपत ते जो हो कमाईदा आहिनि. ढल पिणि इंदी आहे संदुनि पंहिंजे स्तर सां जो पक कंदी आङे केतरि ढल कम्पनी खे भरणी आहे. For example, a domestic company, that has a revenue of less than Rs. 1 crore per annum won’t have to pay this tax, but one that has a revenue of more than Rs. 1 crore per annum will have to pay this tax. इहो पिणि ड॒सयो वयो आहे हिक वाधे महसुल तोर ऐं इहो धारु आहे जुदा जुदा कर जे भांङनि खां. It is also different for international companies, where the corporate tax may be 41.2% if the company has a revenue of less than Rs. 10 million and so on.
There are four different types of corporate tax.
- घटि में घटि बि॒वाटी ढलु:
घटि में घटि बे॒धर जी ढल, या ऐम ऐ टी, बुनियादी तोर हिक वाटि आहे आमदनी ढल विभाग जो कमपनीयूंनि खे घटि में घटि ढल भूगतान करण जो , जो हि हिंअर 18.5% आहे. हिन नमुने जो ढल असर हेटि आंदो वयोआमदनी ढल कोनुन जे विभाग 115 जे ऐ जे देबा॒चो थिअण सां. बहरआल, कम्पनीयूं जो कि मुंझयलु आहिनि आडावत ऐं भिजली बिबागन में से ऐम ऐ टी जे भूगतान खां आझो आहिनि.
Once a company pays the MAT, it can carry the payment forward and set-off (adjust) against regular tax payable during the subsequent five-year period, subject to certain conditions.
- झालर फाईदो ढलु:
Fringe Benefit Tax, or FBT, was a tax that applied to almost every fringe benefit an employer provided to their employees. हिन ढल में , जाम पहलुंनि खे ध्यानु डि॒ञो वेंदो आहे. इन मंझ के आहिनि:
i) मुलाजिम जो सैर ते खर्चु (ऐल टी ऐ), मुलाजिम खुशहाली, पिहाईश ऐं विंदुरु.
ii) को बि रिवाजी आमदफरद या आमदफरद सां लागापो रखिंदड खर्चु जो कि मालिज पारां मेसर थो कराईजे.
iii) मालिक जी पती हिक साबित कयलु फारुग राशी.
iv) मुलाजिम स्टाक विकल्प रिथा (ई ऐस ओ पी अ).
ऐफ बी टी शुरु कई वई हुई भारत सरकार जे निगरानी में अप्रेल 1, 2005 खां. However, the tax was later scrapped in 2009 by then- Finance Minister Pranab Mukherjee during the 2009 Union Budget session.
- वनढणी वर्छायप ढल:
पाईदो विर्छायप ढल पधरी कई वई हुई 2007 जे मर्कजी बजेट जे पिछाईअ ते. It is basically a tax levied on companies based on the dividend they pay to their investors. This tax is applicable on the gross or net income an investor receives from their investment. हिंअर, डी डी टी जा अघ 15% ते विठा आहिनि.
- बैंक रोक डे॒तिलेती ढल:
बैंक रोक डे॒तीलेती ढल अञा हिक धारो तरिको हो ढल जो जा भारत सरकार पारां तयागी वई आहे. This form of taxation was in operation from 2005-2009 until then FM Pranab Mukherjee nullified the tax. हिउ ढल सलाहि थो डि॒ऐ त हर बैंक डेतीलेती (जमा या निकाली) ते ढल मडही वेंदी 0.1% जे अघ ते.
2. अणसिधी ढल:
By definition, indirect taxes are those taxes that are levied on goods or services. They differ from direct taxes because they are not levied on a person who pays them directly to the government, they are instead levied on products and are collected by an intermediary, the person selling the product. The most common examples of indirect tax Indirect tax can be VAT (Value Added Tax), Taxes on Imported Goods, Sales Tax, etc. These taxes are levied by adding them to the price of the service or product, which tends to push the cost of the product up.
अण-सिधे ढल जा मिसाल:
हिउ आहिनि कजहि आम अण-सिधा ढल जो तव्हां भरींदा आहियो.
a) Sales Tax:
As the name suggests, a sales tax is a tax that is levied on the sale of a product. हिउ पदार्थ कजहि ती थो सघे जो भारत में पैदा या आयात कयो वयो ऐं इन हद ताई जे मेसर करयलु सेवा ड॒ई थो सघे. This tax is levied on the seller of the product, who then transfers it onto the person who buys said product, with the sales tax added to the price of the product. The limitation of this tax is that it can be levied only once for a particular product, which means that if the product is sold a second time, sales tax cannot be applied to it.
बुनियादी तोर, मुल्क में समुरा प्रदेश संदुनि पहिंजो विकरो ढल मञिंदा आहिनि ऐं मडहिंदा आहिनि पंहिजे नमुने सां. Besides this, a few states also levy other additional charges like turnover tax, purchase tax, work transaction tax, and the like. इहो पिणि सबब आहे जे थो विकरो ढल जुदा जुजा सरकारन लाई सभनि खां वडो॒ कर कठो करिंदड थिंदो आहे. Also, this tax is levied under both central and state legislation.
b) Service Tax:
जिअं विकरो ढल भारत में विकरो कयलु सामान ते गढयो वेंदो आहे, सागी॒ रित सेवा ढल भारत में मेसर कयलु सेवायूंनि ते मडहो वेंदो आहे. 2015, बजेट जे ऐलान में , इजो नसर कयो वयो त सेवा ढल वधायो वेंदो 12.36% खां 14% ते. इहो लागु नाहे थिंदो सामान ते पर कम्पनीयूं जो सेवा पई मेसर कनि ऐं को कि कठो कयो वेंदी आहे हर महिने या हर चैमासे मेसर कयलु सेवा जे आधार ते. If the establishment is an individual service provider, then the service tax is paid only once the customer pays the bills; however, for companies, the service tax is payable the moment the invoice is raised, irrespective of the customer paying the bill.
An important thing to remember is that since the service at a restaurant is a combination of the food, the waiter, and the premises themselves, it is difficult to pin point what qualifies for service tax. इंन मुंझारे खे सोरण लाई, इहो ऐलान कयो वयो आहे त रेस्टुरेंटनि में सेवा ढल मडही वेंदी जा कुल बील जी 40% थिंदी.
जी ऐस टी - समान ऐं सेवा ढल:
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is the largest reform in India’s indirect tax structure since the market started opening up about 25 years ago. The GST is a consumption-based tax, as it is applicable where consumption takes place. The GST is levied on value-added goods and services at each stage of consumption in the supply chain. The GST payable on the procurement of goods and services can be set off against the GST payable on the supply of goods and services, the merchant will pay the applicable GST rate but can claim it back through the tax credit mechanism.
c) Value Added Tax:
VAT, also known as commercial tax, is not applicable on commodities that are zero-rated (e.g., food and essential drugs) or those that fall under exports. This tax is levied at all the stages of the supply chain, right from the manufacturers, dealers, and distributors to the end user.
The value-added tax is a tax that is levied at the discretion of the state government, and not all states implemented it when it was first announced. The tax is levied on various goods sold in the state, and the amount of the tax is decided by the state itself. For example, in Gujarat, the government split all the goods into various categories called schedules. There are 3 schedules, and each schedule has its own VAT percentage. For Schedule 3 the VAT is 1%, for Schedule 2 the VAT is 5%; and so on. सामान जहिं खे नाहे विरहायो वयो आहे कहिं बि भाङे में संदुनि ते 15% जी वेट लागु थिंदी.
d) Custom duty & Octroi:
When you purchase anything that needs to be imported from another country, a charge is applied to it, and that is the customs duty. It applies to all the products that come in via land, sea, or air. Even if you bring in products bought in another country to India, a customs duty can be levied on them. The purpose of the customs duty is to ensure that all goods entering the country are taxed and paid for. जिअं त कस्टम ढल पक कंदी आहे त धारी मुल्कनि तां मान ते ढल मडिजे, ओक्टोऐ जो मलतब आहे त सामान जो राज्यनि जे सरदहनि खे ओरांगे थो भारत में तहिं ते वाजिबी तोर ढल मडिजे. इहो राज्य सरकार पारां मडहयो वेंदो आहे ऐं इहो तमाम घणो इन रित कमु कंदो आहे जिअं क्सटम डयूटी कंदी आहे.
e) Excise Duty:
हिउ उहा ढल आहे जा मडही वेंदी आहे भारत में संमुरे सामान पैदाकंदड या ठहिंदड मथां. It is different from customs duty because it is applicable only on things produced in India and is also known as the Central Value Added Tax, or CENVAT. हिउ ढल कठो कयो वेंदो आहे सरकार पारां सामान जी ठाहणईंदडनि खां. इहा पिणि उगारे थी सघिजे इन इकाईयूंनि खां जो कि हासिल था कनि ठहयलु सामान ऐं माण्हनि खे रोजगार पई डिं॒दा आहिनि सामान खे ठाहिंदड खां पाणवटि आमदफरद करण लाई.
The Central Excise Rule set by the central government suggests that every person that produces or manufactures any 'excisable goods', or who stores such goods in a warehouse, will have to pay the duty applicable to such goods. Under this rule, no excisable goods, on which any duty is payable, will be allowed to move without payment of duty from any place where they are produced or manufactured.